Node Lifecycle Controller Manager源码解析
Node Lifecycle Controller根据node的lease和node status更新时间,决定是否驱逐node上的pod或设置taint,设置node ready condition为unknown。
并且根据整个集群状态和zone里不同数量的unready node,设置不同的node速率-来添加taint或执行驱逐pod。
该解析为kubernetes版本为1.18.6
1 启动过程
controller manager创建一个goroutine启动Node Lifecycle controller,node lifecycle controller启动函数为startNodeLifecycleController 在cmd\kube-controller-manager\app\core.go。
func startNodeLifecycleController(ctx ControllerContext) (http.Handler, bool, error) {
lifecycleController, err := lifecyclecontroller.NewNodeLifecycleController(
ctx.InformerFactory.Coordination().V1().Leases(),
ctx.InformerFactory.Core().V1().Pods(),
ctx.InformerFactory.Core().V1().Nodes(),
ctx.InformerFactory.Apps().V1().DaemonSets(),
// node lifecycle controller uses existing cluster role from node-controller
ctx.ClientBuilder.ClientOrDie("node-controller"),
ctx.ComponentConfig.KubeCloudShared.NodeMonitorPeriod.Duration, //默认为5s 取决于--node-monitor-period
ctx.ComponentConfig.NodeLifecycleController.NodeStartupGracePeriod.Duration,//默认为1min 取决于--node-startup-grace-period
ctx.ComponentConfig.NodeLifecycleController.NodeMonitorGracePeriod.Duration,//默认为40s 取决于--node-monitor-grace-period
ctx.ComponentConfig.NodeLifecycleController.PodEvictionTimeout.Duration,//默认为5min 取决于--pod-eviction-timeout
ctx.ComponentConfig.NodeLifecycleController.NodeEvictionRate,//默认为0.1 取决于--node-eviction-rate
ctx.ComponentConfig.NodeLifecycleController.SecondaryNodeEvictionRate,//默认为0.01 取决于--secondary-node-eviction-rate
ctx.ComponentConfig.NodeLifecycleController.LargeClusterSizeThreshold,//默认为50 取决于--large-cluster-size-threshold
ctx.ComponentConfig.NodeLifecycleController.UnhealthyZoneThreshold,//默认为0.55 取决于--unhealthy-zone-threshold
ctx.ComponentConfig.NodeLifecycleController.EnableTaintManager, //默认为true 取决于 --enable-taint-manager
)
if err != nil {
return nil, true, err
}
go lifecycleController.Run(ctx.Stop)
return nil, true, nil
}2 相关的命令行参数
Node Lifecycle controller相关的命令行参数有这些
--enable-taint-manager
WARNING: Beta feature. If set to true enables NoExecute Taints and will evict all not-tolerating Pod running on
Nodes tainted with this kind of Taints. (default true)
启用在unready时候为node添加taint和ready时候移除相关taint和进行驱逐pod不能容忍NoExecute Taints
--large-cluster-size-threshold int32
Number of nodes from which NodeController treats the cluster as large for the eviction logic purposes.
--secondary-node-eviction-rate is implicitly overridden to 0 for clusters this size or smaller. (default 50)
node数量超过多少认为是large-cluster
--node-eviction-rate float32
Number of nodes per second on which pods are deleted in case of node failure when a zone is healthy (see
--unhealthy-zone-threshold for definition of healthy/unhealthy). Zone refers to entire cluster in non-multizone
clusters. (default 0.1)
在zone healthy时候(unhealthy node数量比小于 --unhealthy-zone-threshold)的驱逐速率
--node-monitor-grace-period duration
Amount of time which we allow running Node to be unresponsive before marking it unhealthy. Must be N times more
than kubelet's nodeStatusUpdateFrequency, where N means number of retries allowed for kubelet to post node
status. (default 40s)
多久node没有响应认为node为unhealthy
--node-startup-grace-period duration
Amount of time which we allow starting Node to be unresponsive before marking it unhealthy. (default 1m0s)
多久允许刚启动的node未响应,认为unhealthy
--pod-eviction-timeout duration
The grace period for deleting pods on failed nodes. (default 5m0s)
当node unhealthy时候多久删除上面的pod(只在taint manager未启用时候生效)
--secondary-node-eviction-rate float32
Number of nodes per second on which pods are deleted in case of node failure when a zone is unhealthy (see
--unhealthy-zone-threshold for definition of healthy/unhealthy). Zone refers to entire cluster in non-multizone
clusters. This value is implicitly overridden to 0 if the cluster size is smaller than
--large-cluster-size-threshold. (default 0.01)
当zone unhealthy时候,一秒内多少个node进行驱逐node上pod
--unhealthy-zone-threshold float32
Fraction of Nodes in a zone which needs to be not Ready (minimum 3) for zone to be treated as unhealthy.
(default 0.55)
多少比例的unhealthy node认为zone unhealthy
--node-monitor-period duration
The period for syncing NodeStatus in NodeController. (default 5s)
更新release资源的周期3 数据结构
type Controller struct {
.........
//周期性主动扫描到的node存在这里,用于对比新增加的node、删除的node
knownNodeSet map[string]*v1.Node
// per Node map storing last observed health together with a local time when it was observed.
//周期性扫描node,从shareinformer获取node status保存在这里
nodeHealthMap *nodeHealthMap
// evictorLock protects zonePodEvictor and zoneNoExecuteTainter.
// TODO(#83954): API calls shouldn't be executed under the lock.
evictorLock sync.Mutex
// workers that evicts pods from unresponsive nodes.
//未启用taints manager时使用,存放node上pod是否已经执行驱逐的状态, 从这读取node eviction的状态是evicted、tobeeviced
nodeEvictionMap *nodeEvictionMap
//未启用taints manager时使用, zone的需要pod evictor的node列表
zonePodEvictor map[string]*scheduler.RateLimitedTimedQueue
// workers that are responsible for tainting nodes.
//启用taints manage时使用,存放需要更新taint的unready node列表--令牌桶队列
zoneNoExecuteTainter map[string]*scheduler.RateLimitedTimedQueue
//存放每个zone的健康状态,有stateFullDisruption、statePartialDisruption、stateNormal、stateInitial
zoneStates map[string]ZoneState
// Value controlling Controller monitoring period, i.e. how often does Controller
// check node health signal posted from kubelet. This value should be lower than
// nodeMonitorGracePeriod.
// TODO: Change node health monitor to watch based.
// 主动扫描所有node的周期
nodeMonitorPeriod time.Duration
// When node is just created, e.g. cluster bootstrap or node creation, we give
// a longer grace period.
// node刚注册时候的,认为node unready的超时时间
nodeStartupGracePeriod time.Duration
// Controller will not proactively sync node health, but will monitor node
// health signal updated from kubelet. There are 2 kinds of node healthiness
// signals: NodeStatus and NodeLease. NodeLease signal is generated only when
// NodeLease feature is enabled. If it doesn't receive update for this amount
// of time, it will start posting "NodeReady==ConditionUnknown". The amount of
// time before which Controller start evicting pods is controlled via flag
// 'pod-eviction-timeout'.
// Note: be cautious when changing the constant, it must work with
// nodeStatusUpdateFrequency in kubelet and renewInterval in NodeLease
// controller. The node health signal update frequency is the minimal of the
// two.
// There are several constraints:
// 1. nodeMonitorGracePeriod must be N times more than the node health signal
// update frequency, where N means number of retries allowed for kubelet to
// post node status/lease. It is pointless to make nodeMonitorGracePeriod
// be less than the node health signal update frequency, since there will
// only be fresh values from Kubelet at an interval of node health signal
// update frequency. The constant must be less than podEvictionTimeout.
// 2. nodeMonitorGracePeriod can't be too large for user experience - larger
// value takes longer for user to see up-to-date node health.
// node的不更新status或者lease的持续时间,超过这个时间会将node的ready condition改为unknown
nodeMonitorGracePeriod time.Duration
// node unready之后多久执行驱逐node上的pod
podEvictionTimeout time.Duration
// zone正常时候的 每秒多少个node去执行驱逐/添加taint
evictionLimiterQPS float32
// zone为statePartialDisruption时候且节点数量大于largeClusterThreshold 每秒多少个node去执行驱逐/添加taint
secondaryEvictionLimiterQPS float32
// 多少个节点数认为大集群, 这个数值用来判断是否在zone为statePartialDisruption时候,将每秒多少个node去执行驱逐/添加taint设置为0
largeClusterThreshold int32
// unready node超出多少比例,认为zone是statePartialDisruption
unhealthyZoneThreshold float32
// if set to true Controller will start TaintManager that will evict Pods from
// tainted nodes, if they're not tolerated.
runTaintManager bool
// 不限速的workqueue
nodeUpdateQueue workqueue.Interface
// 具有限速和指数回退策略的workqueue
podUpdateQueue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface
}4 队列
这里使用的队列有:
workqueue
- nodeUpdateQueue
- podUpdateQueue
RateLimitedTimedQueue
- zonePodEvictor
- zoneNoExecuteTainter
队列后面再详细深入解析
5 controller初始化
初始化做这几个事情:
- 初始化数据结构和设置各个字段值
- 设置监听pod事件的handler,将pod item添加到podUpdateQueue里(如果启用taint manager,还会添加taint manager相关的handler,将pod添加到taint manager里的podUpdateQueue)
- pod sharedinformer中添加新的 indexers,用于查找node的上的所有pods。
- 初始化event recorder,用于发送event到apiserver
- 启用taint manager情况下,初始化taintManager,并添加node事件的handler–由taint manager处理
- 添加node事件handler–将node添加到nodeUpdateQueue
// NewNodeLifecycleController returns a new taint controller.
func NewNodeLifecycleController(
leaseInformer coordinformers.LeaseInformer,
podInformer coreinformers.PodInformer,
nodeInformer coreinformers.NodeInformer,
daemonSetInformer appsv1informers.DaemonSetInformer,
kubeClient clientset.Interface,
nodeMonitorPeriod time.Duration,
nodeStartupGracePeriod time.Duration,
nodeMonitorGracePeriod time.Duration,
podEvictionTimeout time.Duration,
evictionLimiterQPS float32,
secondaryEvictionLimiterQPS float32,
largeClusterThreshold int32,
unhealthyZoneThreshold float32,
runTaintManager bool,
) (*Controller, error) {
if kubeClient == nil {
klog.Fatalf("kubeClient is nil when starting Controller")
}
//初始化event recorder
eventBroadcaster := record.NewBroadcaster()
recorder := eventBroadcaster.NewRecorder(scheme.Scheme, v1.EventSource{Component: "node-controller"})
eventBroadcaster.StartLogging(klog.Infof)
klog.Infof("Sending events to api server.")
eventBroadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(
&v1core.EventSinkImpl{
Interface: v1core.New(kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient()).Events(""),
})
if kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient().GetRateLimiter() != nil {
ratelimiter.RegisterMetricAndTrackRateLimiterUsage("node_lifecycle_controller", kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient().GetRateLimiter())
}
nc := &Controller{
kubeClient: kubeClient,
now: metav1.Now,
knownNodeSet: make(map[string]*v1.Node),
nodeHealthMap: newNodeHealthMap(), //存放发现的node的health数据
nodeEvictionMap: newNodeEvictionMap(),
recorder: recorder,
nodeMonitorPeriod: nodeMonitorPeriod, //默认为5s
nodeStartupGracePeriod: nodeStartupGracePeriod, //默认一分钟
nodeMonitorGracePeriod: nodeMonitorGracePeriod, //默认40s
zonePodEvictor: make(map[string]*scheduler.RateLimitedTimedQueue),//未启用taints manage, zone里需要pod evicted的node列表,令牌桶速度限制队列
zoneNoExecuteTainter: make(map[string]*scheduler.RateLimitedTimedQueue),//启用taints manage,需要更新taint的unhealy node列表,令牌桶速度限制队列
nodesToRetry: sync.Map{},
zoneStates: make(map[string]ZoneState), //存放每个zone的状态
podEvictionTimeout: podEvictionTimeout, //默认为5分钟
evictionLimiterQPS: evictionLimiterQPS, //默认为0.1
secondaryEvictionLimiterQPS: secondaryEvictionLimiterQPS, //默认为0.01
largeClusterThreshold: largeClusterThreshold, //默认为50
unhealthyZoneThreshold: unhealthyZoneThreshold, //默认为0.55
runTaintManager: runTaintManager, //默认为true
nodeUpdateQueue: workqueue.NewNamed("node_lifecycle_controller"), //node变更时候,会加入队列,然后进行taint添加、更新
podUpdateQueue: workqueue.NewNamedRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.DefaultControllerRateLimiter(), "node_lifecycle_controller_pods"), //有队列和限速,pod变更时候,会加入队列,用来将pod进行驱逐或者pod condition 改为ready false
}
nc.enterPartialDisruptionFunc = nc.ReducedQPSFunc
nc.enterFullDisruptionFunc = nc.HealthyQPSFunc
nc.computeZoneStateFunc = nc.ComputeZoneState
podInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
pod := obj.(*v1.Pod)
nc.podUpdated(nil, pod)
if nc.taintManager != nil {
nc.taintManager.PodUpdated(nil, pod)
}
},
UpdateFunc: func(prev, obj interface{}) {
prevPod := prev.(*v1.Pod)
newPod := obj.(*v1.Pod)
nc.podUpdated(prevPod, newPod)
if nc.taintManager != nil {
nc.taintManager.PodUpdated(prevPod, newPod)
}
},
DeleteFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
pod, isPod := obj.(*v1.Pod)
// We can get DeletedFinalStateUnknown instead of *v1.Pod here and we need to handle that correctly.
if !isPod {
deletedState, ok := obj.(cache.DeletedFinalStateUnknown)
if !ok {
klog.Errorf("Received unexpected object: %v", obj)
return
}
pod, ok = deletedState.Obj.(*v1.Pod)
if !ok {
klog.Errorf("DeletedFinalStateUnknown contained non-Pod object: %v", deletedState.Obj)
return
}
}
nc.podUpdated(pod, nil)
if nc.taintManager != nil {
nc.taintManager.PodUpdated(pod, nil)
}
},
})
nc.podInformerSynced = podInformer.Informer().HasSynced
//sharedinformer中添加新的indexers
podInformer.Informer().AddIndexers(cache.Indexers{
nodeNameKeyIndex: func(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {
pod, ok := obj.(*v1.Pod)
if !ok {
return []string{}, nil
}
if len(pod.Spec.NodeName) == 0 {
return []string{}, nil
}
return []string{pod.Spec.NodeName}, nil
},
})
podIndexer := podInformer.Informer().GetIndexer()
nc.getPodsAssignedToNode = func(nodeName string) ([]*v1.Pod, error) {
objs, err := podIndexer.ByIndex(nodeNameKeyIndex, nodeName)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
pods := make([]*v1.Pod, 0, len(objs))
for _, obj := range objs {
pod, ok := obj.(*v1.Pod)
if !ok {
continue
}
pods = append(pods, pod)
}
return pods, nil
}
nc.podLister = podInformer.Lister()
if nc.runTaintManager {
podGetter := func(name, namespace string) (*v1.Pod, error) { return nc.podLister.Pods(namespace).Get(name) }
nodeLister := nodeInformer.Lister()
nodeGetter := func(name string) (*v1.Node, error) { return nodeLister.Get(name) }
nc.taintManager = scheduler.NewNoExecuteTaintManager(kubeClient, podGetter, nodeGetter, nc.getPodsAssignedToNode)
nodeInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: nodeutil.CreateAddNodeHandler(func(node *v1.Node) error {
nc.taintManager.NodeUpdated(nil, node)
return nil
}),
UpdateFunc: nodeutil.CreateUpdateNodeHandler(func(oldNode, newNode *v1.Node) error {
nc.taintManager.NodeUpdated(oldNode, newNode)
return nil
}),
DeleteFunc: nodeutil.CreateDeleteNodeHandler(func(node *v1.Node) error {
nc.taintManager.NodeUpdated(node, nil)
return nil
}),
})
}
klog.Infof("Controller will reconcile labels.")
nodeInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: nodeutil.CreateAddNodeHandler(func(node *v1.Node) error {
nc.nodeUpdateQueue.Add(node.Name)
nc.nodeEvictionMap.registerNode(node.Name)
return nil
}),
UpdateFunc: nodeutil.CreateUpdateNodeHandler(func(_, newNode *v1.Node) error {
nc.nodeUpdateQueue.Add(newNode.Name)
return nil
}),
DeleteFunc: nodeutil.CreateDeleteNodeHandler(func(node *v1.Node) error {
nc.nodesToRetry.Delete(node.Name)
nc.nodeEvictionMap.unregisterNode(node.Name)
return nil
}),
})
nc.leaseLister = leaseInformer.Lister()
nc.leaseInformerSynced = leaseInformer.Informer().HasSynced
nc.nodeLister = nodeInformer.Lister()
nc.nodeInformerSynced = nodeInformer.Informer().HasSynced
nc.daemonSetStore = daemonSetInformer.Lister()
nc.daemonSetInformerSynced = daemonSetInformer.Informer().HasSynced
return nc, nil
}6 运行
首先会等待leaseInformer、nodeInformer、podInformerSynced、daemonSetInformerSynced同步完成。
如果启用taint manager,goroutine一直执行nc.taintManager.Run(stopCh)–运行taint manager,在下一篇介绍。
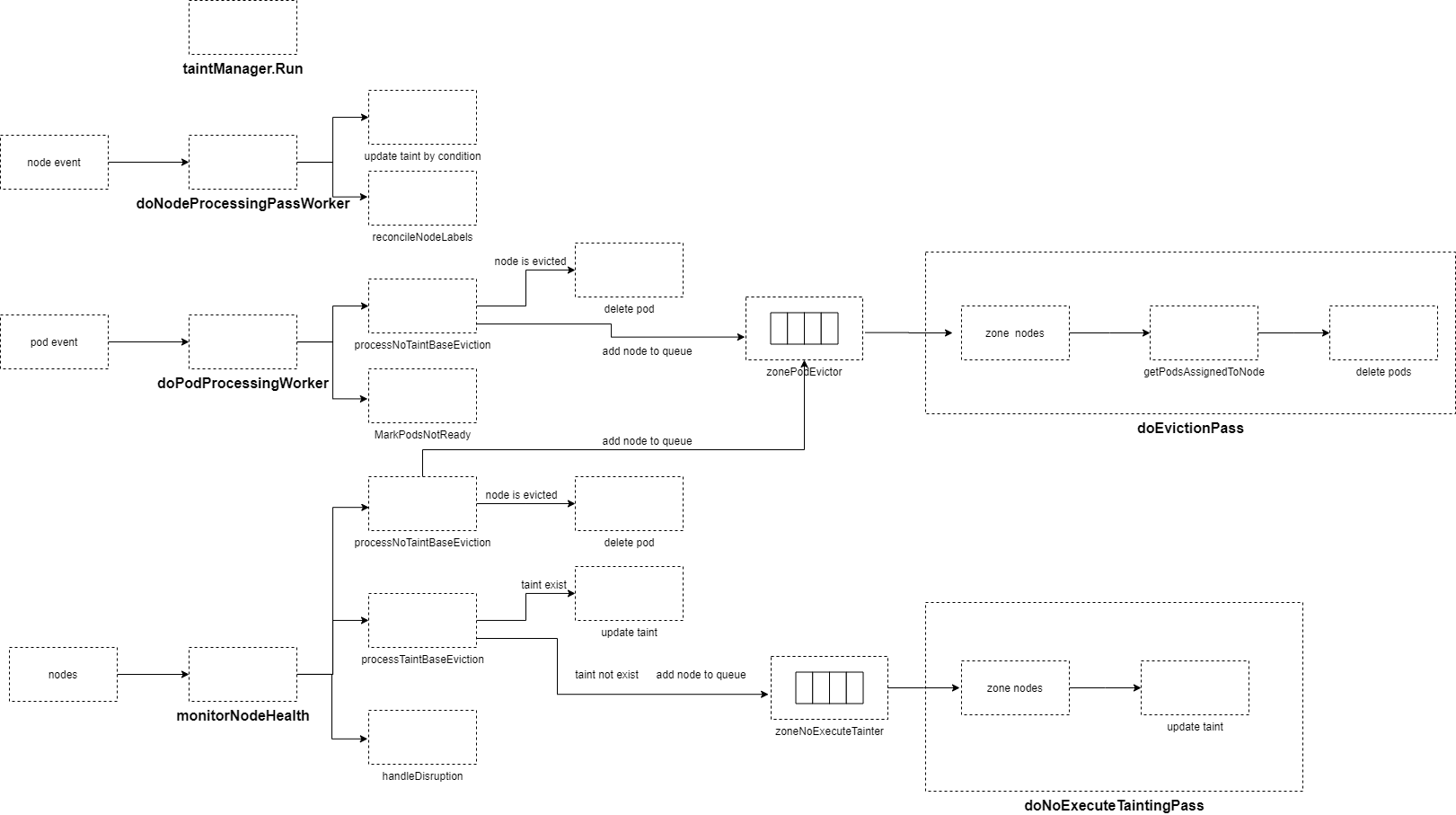
启动8个goroutine每秒执行nc.doNodeProcessingPassWorker–消费nodeUpdateQueue,更新node的NoSchedule taint和label。
启动4个goroutine每秒执行doPodProcessingWorker–消费podUpdateQueue,当pod所在的node为unready,将pod condition设为ready false。在不启用taint manager时候,且node为unready,则对该pod进行删除,如果该node unready持续时间超过pod-evicted-timeout,则node加入到zonePodEvictor。
启用taint manager启动goroutine每100ms执行doNoExecuteTaintingPass–消费zoneNoExecuteTainter队列,根据node的ready condition,来更新node的noexecute taints。
未启用taint manager启动goroutine每100ms执行doEvictionPass–消费zonePodEvictor队列,删除node上的所有pod,更新nodeEvictionMap标记node为evicted。
启动goroutine每--node-monitor-period时间,执行monitorNodeHealth– 周期性的检查所有node状态,如果kubelet没有更新status.condition ready.lastHeartbeatTime或lease里的renew time 超过nodeMonitorGracePeriod,则更新node status为unknown,并根据zone里node unready的数量,设置每秒不同的数量node进行驱逐pod或添加taint。
// Run starts an asynchronous loop that monitors the status of cluster nodes.
func (nc *Controller) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
klog.Infof("Starting node controller")
defer klog.Infof("Shutting down node controller")
if !cache.WaitForNamedCacheSync("taint", stopCh, nc.leaseInformerSynced, nc.nodeInformerSynced, nc.podInformerSynced, nc.daemonSetInformerSynced) {
return
}
//pod是否能够toleration上的tains,不能就进行驱逐pod
if nc.runTaintManager {
go nc.taintManager.Run(stopCh)
}
// Close node update queue to cleanup go routine.
defer nc.nodeUpdateQueue.ShutDown()
defer nc.podUpdateQueue.ShutDown()
// Start workers to reconcile labels and/or update NoSchedule taint for nodes.
for i := 0; i < scheduler.UpdateWorkerSize; i++ {
// Thanks to "workqueue", each worker just need to get item from queue, because
// the item is flagged when got from queue: if new event come, the new item will
// be re-queued until "Done", so no more than one worker handle the same item and
// no event missed.
go wait.Until(nc.doNodeProcessingPassWorker, time.Second, stopCh)
}
for i := 0; i < podUpdateWorkerSize; i++ {
go wait.Until(nc.doPodProcessingWorker, time.Second, stopCh)
}
if nc.runTaintManager {
// Handling taint based evictions. Because we don't want a dedicated logic in TaintManager for NC-originated
// taints and we normally don't rate limit evictions caused by taints, we need to rate limit adding taints.
go wait.Until(nc.doNoExecuteTaintingPass, scheduler.NodeEvictionPeriod, stopCh)
} else {
// Managing eviction of nodes:
// When we delete pods off a node, if the node was not empty at the time we then
// queue an eviction watcher. If we hit an error, retry deletion.
go wait.Until(nc.doEvictionPass, scheduler.NodeEvictionPeriod, stopCh)
}
// Incorporate the results of node health signal pushed from kubelet to master.
go wait.Until(func() {
if err := nc.monitorNodeHealth(); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Error monitoring node health: %v", err)
}
}, nc.nodeMonitorPeriod, stopCh)
<-stopCh
}6.1 doNodeProcessingPassWorker
node更新、添加事件,都会添加到nodeUpdateQueue中。
doNodeProcessingPassWorker从nodeUpdateQueue获取一个node,根据node status里的condition,设置不同的noschedule taint和设置node label。
对该node执行doNoScheduleTaintingPass–根据node status里的condition设置taint
- node.status.Conditions 有type为ready的condition。如果这个condition.status为fasle,设置
key node.kubernetes.io/not-ready,Effect为noschedule的taint;这个condition.status为unknown,设置key node.kubernetes.io/unreachable,Effect为noschedule - node.status.Conditions 有type为MemoryPressure的condition。如果这个condition.status为true,设置
key node.kubernetes.io/memory-pressure,Effect为noschedule的taint - node.status.Conditions 有type为DiskPressure的condition。如果这个condition.status为true,设置
key node.kubernetes.io/disk-pressure,Effect为noschedule的taint - node.status.Conditions 有type为NetworkUnavailable的condition。如果这个condition.status为true,设置
key node.kubernetes.io/network-unavailable,Effect为noschedule的taint - node.status.Conditions 有type为PIDPressure的condition。如果这个condition.status为true,设置
key node.kubernetes.io/pid-pressure,Effect为noschedule的taint - node.Spec.Unschedulable有值,则设置
key node.kubernetes.io/unschedulable Effect为noschedule的taint
执行reconcileNodeLabels–当os和arch label存在,确保一致
- 缓存中获取node,确认node是否存在,node不存在,直接返回
- 检查node label是否为空,为空直接返回
- 如果存在label “beta.kubernetes.io/os”,则设置label “kubernetes.io/os"值是一样的,否则忽略
- 如果存在label “beta.kubernetes.io/arch”,则设置label “kubernetes.io/arch"值是一样,否则忽略
处理完执行Done,将node从workqueue中移除。
总结
当node ready condition.status为fasle,会设置key node.kubernetes.io/not-ready,Effect为noschedule 的taint。如果启用了taint manager,还会设置key node.kubernetes.io/not-ready,Effect为noExecute 的taint(在monitorNodeHealth里processTaintBaseEviction里执行的)
当node ready condition.status为unknown,会设置key node.kubernetes.io/unreachable,Effect为noschedule 的taint。如果启用了taint manager,还会设置key node.kubernetes.io/unreachable,Effect为noExecute 的taint(在monitorNodeHealth里processTaintBaseEviction里执行的)
label “beta.kubernetes.io/os”、“kubernetes.io/os"和beta.kubernetes.io/arch”、“kubernetes.io/arch"在kubelet node注册的时候就会有,这里只是确保beta.kubernetes.io/*存在,kubernetes.io/*也要存在。
6.2 doPodProcessingWorker
当pod新生成且pod绑定了node(spec.NodeName存在)、pod更新且绑定的node发生变化都会添加到podUpdateQueue。
doPodProcessingWorker从podUpdateQueue读取一个pod,执行processPod–如果pod绑定node为unready,则将这个pod的ready condition设置为false,并更新transitionTimestamp。未启用taint manager,pod绑定node为unready,先驱逐这个pod,然后将node添加到zonePodEvictor
从缓存中获取pod,得到pod绑定的node名字。
判断node是否在nodeHealthMap里,如果不在,直接返回。
获取nodeHealthMap里最后发现node的ready condition,如果为空,直接返回。
如果未启用taint manager,执行processNoTaintBaseEviction
- node最后发现ReadyCondition为false,如果nodeHealthMap里的readyTransitionTimestamp加上podEvictionTimeout的时间是过去的时间–ReadyCondition为false状态已经持续了至少podEvictionTimeout,执行evictPods。
- node最后发现ReadyCondition为unknown,如果nodeHealthMap里的readyTransitionTimestamp加上podEvictionTimeout的时间是过去的时间–ReadyCondition为false状态已经持续了至少podEvictionTimeout,执行evictPods。
- node最后发现ReadyCondition为true,则执行cancelPodEviction–在nodeEvictionMap设置status为unmarked,然后node从zonePodEvictor队列中移除。
- evictPods–先从nodeEvictionMap获取node驱逐的状态,如果是evicted说明node已经发生驱逐,则把node上的这个pod删除。否则设置状态为toBeEvicted,然后node加入zonePodEvictor队列等待执行驱逐pod。
node最后发现ReadyCondition不为true,执行MarkPodsNotReady–如果pod的ready condition不为false, 将pod的ready condition设置为false,并更新LastTransitionTimestamp;否则不更新pod
为什么node不在nodeHealthMap里或nodeHealthMap里最后发现node的ready condition为空,就直接返回?
node不在nodeHealthMap里,说明node被删除或者controller manager刚运行 node信息还未收集–monitorNodeHealth刚运行。nodeHealthMap里最后发现node的ready condition为空,说明node是刚添加。因为我们要获取最后保存的node状态来决定采取的动作,所以这里直接返回。
为什么只对未启用taint manager采取动作,启用的taint manager未采取动作?
在NewNodeLifecycleController里定义了, 在启用taint manager情况下,pod发生变化都会将pod添加进taintManager里的podUpdateQueue,由taint manager进行处理,所以不在这里处理。
6.3 执行驱逐pod
启用taint manager 执行doNoExecuteTaintingPass–添加NoExecute的taint。这里不执行驱逐,驱逐单独在taint manager里处理。
doNoExecuteTaintingPass是一个令牌桶限速队列
- 遍历zoneNoExecuteTainter,获得一个zone的node队列,从队列中获取一个node,执行下面步骤
- 从缓存中获取node
- 如果node ready condition为false,移除“node.kubernetes.io/unreachable”的taint,添加“node.kubernetes.io/not-ready” 的taint,Effect为NoExecute。
- 如果node ready condition为unknown,移除“node.kubernetes.io/not-ready” 的taint,添加“node.kubernetes.io/unreachable” 的taint,Effect为NoExecute。
未启用taint manager 执行doEvictionPass–对node上的所有pod进行驱逐。
doEvictionPass是一个令牌桶限速队列,+加入这个队列的node都是 unready状态持续时间大于podEvictionTimeout。
- 遍历zonePodEvictor,获取一个zone里的node队列,从队列中获取一个node,执行下面步骤
- 获取node的uid,从缓存中获取node上的所有pod
- 执行DeletePods–删除daemonset之外的所有pod,保留daemonset的pod
- 遍历所由的pod,检查pod绑定的node是否跟提供的一样,不一样则跳过这个pod
- 执行SetPodTerminationReason–设置pod Status.Reason为
NodeLost,Status.Message为"Node %v which was running pod %v is unresponsive",并更新pod。 - 如果pod 设置了DeletionGracePeriodSeconds,说明pod已经被删除,则跳过这个pod
- 判断pod是否为daemonset的pod,如果是则跳过这个pod
- 删除这个pod
- 在nodeEvictionMap设置node的状态为evicted
6.4 主动扫描node健康状态monitorNodeHealth
每隔nodeMonitorPeriod周期,执行一次monitorNodeHealth,维护node状态和zone的状态,更新未响应的node–设置node status为unknown和根据集群不同状态设置zone的速率。
6.4.1 node分类并初始化
从缓存中获取所有node列表,借助两个字段knownNodeSet(用来存放已经发现的node集合)和zoneStates(用来存储已经发现zone的状态–状态有Initial、Normal、FullDisruption、PartialDisruption)来进行对node进行分类,分为新加的–add、删除的deleted、新的zone node–newZoneRepresentatives。
对新发现的zone进行初始化–启用taint manager,设置执行node设置taint 队列zoneNoExecuteTainter(存放node为unready,需要添加taint)的速率为evictionLimiterQPS。未启用taint manager,设置安排node执行驱逐队列zonePodEvictor(存放zone里的需要执行pod evictor的node列表)的速率evictionLimiterQPS。同时在zoneStates里设置zone状态为stateInitial。
对新发现的node,添加到knownNodeSet,同时在zoneStates里设置zone状态为stateInitial,如果node的所属的zone未初始化,则进行初始化。启用taint manager,标记node为健康的–移除node上unreachable和notready taint(如果存在),从zoneNoExecuteTainter(存放node为unready,需要添加taint)队列中移除(如果存在)。未启用taint manager,初始化nodeEvictionMap(存放node驱逐执行pod的进度)–设置node的状态为unmarked,从zonePodEvictor(存放zone的需要pod evictor的node列表)队列中移除。
对删除的node,发送一个RemovingNode事件并从knownNodeSet里移除。
6.4.2 处理node status
超时时间
如果当前node的ready condition为空,说明node刚注册,所以它的超时时间为nodeStartupGracePeriod,否则它的超时时间为nodeMonitorGracePeriod。
心跳时间
最后的心跳时间(probeTimestamp和readyTransitionTimestamp),由下面规则从上往下执行。
如果node刚注册,则nodeHealthMap保存的probeTimestamp和readyTransitionTimestamp都为node的创建时间。
如果nodeHealthMap里没有该node数据,则probeTimestamp和readyTransitionTimestamp都为现在。
如果nodeHealthMap里的 ready condition没有,而现在有ready condition,则probeTimestamp和readyTransitionTimestamp都为现在,status为现在的status。
如果nodeHealthMap里的有ready condition,而现在的ready condition没有,说明发生了未知的异常情况(一般不会发生,只是预防性的代码),则probeTimestamp和readyTransitionTimestamp都为现在,status为现在的status。
如果nodeHealthMap里有ready condition,而现在的ready condition也有,且保存的LastHeartbeatTime与现在不一样。probeTimestamp为现在、status为现在的status。 如果保存的LastTransitionTime与现在的不一样,说明node状态发生了变化,则设置nodeHealthMap的readyTransitionTimestamp为现在。
如果现在的lease存在,且lease的RenewTime在nodeHealthMap保存的RenewTime之后,或者nodeHealthMap里不存在。则probeTimestamp为现在,保存现在lease到nodeHealthMap里。
尝试更新node状态
如果probeTimestamp加上超时时间,在现在之前–即status状态更新已经超时,则会更新update node。
更新ready、memorypressure、diskpressure、pidpressure的condition为:
相应condition不存在
v1.NodeCondition{
Type: nodeConditionType,//上面的四种类型
Status: v1.ConditionUnknown,// unknown
Reason: "NodeStatusNeverUpdated",
Message: "Kubelet never posted node status.",
LastHeartbeatTime: node.CreationTimestamp,//node创建时间
LastTransitionTime: nowTimestamp, //现在时间
}相应的condition存在
currentCondition.Status = v1.ConditionUnknown
currentCondition.Reason = "NodeStatusUnknown"
currentCondition.Message = "Kubelet stopped posting node status."
currentCondition.LastTransitionTime = nowTimestamp如果现在node与之前的node不一样的–发生了更新,则对node执行update。
update成功,同时更新nodeHealthMap上的状态–readyTransitionTimestamp改为现在,status改为现在的node.status。
对unready node进行处理–驱逐pod
node当前的ReadyCondition–执行尝试更新node状态之后的node的ReadyCondition
node最后发现ReadyCondition–执行尝试更新node状态之前node的ReadyCondition
如果当前的ReadyCondition不为空,执行下面操作
- 从缓存中获取node上pod列表
- 如果启用taint manager,执行processTaintBaseEviction–根据node最后发现ReadyCondition 对node的taint进行操作
- node最后发现ReadyCondition为false,如果已经有“node.kubernetes.io/unreachable”的taint,将该taint删除,添加“node.kubernetes.io/not-ready” 的taint。否则将node添加到zoneNoExecuteTainter队列中,等待添加taint。
- node最后发现ReadyCondition为unknown,如果已经有“node.kubernetes.io/not-ready” 的taint,将该taint删除,添加“node.kubernetes.io/unreachable”的taint。否则将node添加到zoneNoExecuteTainter队列中,等待添加taint。
- node最后发现ReadyCondition为true,移除“node.kubernetes.io/not-ready” 和“node.kubernetes.io/unreachable”的taint,如果存在的话,同时从zoneNoExecuteTainter队列中移除。
- 未启用taint manager,则执行processNoTaintBaseEviction
- node最后发现ReadyCondition为false,nodeHealthMap里的readyTransitionTimestamp加上podEvictionTimeout的时间是过去的时间–ReadyCondition为false状态已经持续了至少podEvictionTimeout,执行evictPods。
- node最后发现ReadyCondition为unknown,nodeHealthMap里的readyTransitionTimestamp加上podEvictionTimeout的时间是过去的时间–ReadyCondition为false状态已经持续了至少podEvictionTimeout,执行evictPods。
- node最后发现ReadyCondition为true,则执行cancelPodEviction–在nodeEvictionMap设置status为unmarked,然后node从zonePodEvictor队列中移除。
- evictPods–先从nodeEvictionMap获取node驱逐的状态,如果是evicted说明node已经发生驱逐,则把node上所有的pod删除。否则设置状态为toBeEvicted,然后node加入zonePodEvictor队列等待执行驱逐pod。
这里有个疑问:
为什么要用observedReadyCondition 而不用currentReadyCondition,observedReadyCondition和currentReadyCondition不一定一样?
比如node挂了currentReadyCondition变为unknown,而observedReadyCondition为ready
这样明显有问题,这一周期不会做驱逐或taint,下一周期observedReadyCondition和currentReadyCondition都为unknown 一定会驱逐pod或添加taint。
可能考虑nodeMonitorPeriod都很短,不立马执行驱逐或taint没有什么大问题。
6.4.3 集群健康状态处理
每个zone有四种状态,stateInitial(刚加入的zone)、stateFullDisruption(全挂)、statePartialDisruption(挂的node比例超出了unhealthyZoneThreshold)、stateNormal(剩下的所有情况)
allAreFullyDisrupted代表现在所有zone状态stateFullDisruption全挂
allWasFullyDisrupted为true代表过去所有zone状态stateFullDisruption全挂
集群状态有四种:
- allAreFullyDisrupted为true allWasFullyDisrupted为true
- allAreFullyDisrupted为true allWasFullyDisrupted为false
- allAreFullyDisrupted为false allWasFullyDisrupted为true
- allAreFullyDisrupted为false allWasFullyDisrupted为false
计算现在集群的状态
遍历现在所有的zone,每个zone遍历所有node的ready condition,计算出zone的状态。
根据zone的状态设置allAreFullyDisrupted的值
如果zone不在zoneStates,添加进zoneStates并设置状态为stateInitial
计算过去集群的状态
从zoneStates读取保存的zone列表,如果不在现在的zone列表里,则从zoneStates移除
根据zoneStates里保存的zone状态设置allWasFullyDisrupted值
设置zone 每秒安排多少个node来执行taint或驱逐
当allAreFullyDisrupted为false allWasFullyDisrupted为true–之前zone未全挂,现在所有zone全挂。
遍历所有node,设置node为正常状态。
- 启用taint manager,执行markNodeAsReachable–移除“node.kubernetes.io/not-ready”和“node.kubernetes.io/unreachable”的taint,如果存的话,同时从zoneNoExecuteTainter队列中移除
- 未启用taint manager,执行cancelPodEviction–在nodeEvictionMap设置status为unmarked,然后node从zonePodEvictor队列中移除
从zoneStates读取保存的zone列表,设置zone 每秒安排多少个node来执行taint或驱逐
- 启用taint manager,设置zoneNoExecuteTainter的速率为0
- 未启用taint manager, 设置zonePodEvictor的速率为0
设置所有zoneStates里的zone为stateFullDisruption
当 allAreFullyDisrupted为true allWasFullyDisrupted为false–过去所有zone全挂,现在所有zone未全挂
- 遍历所有node更新nodeHealthMap里的probeTImestamp、readyTransitiontimestamp为现在的时间戳
- 遍历zoneStates,重新评估zone的每秒安排多少个node来执行taint或驱逐
- 当zone的状态为stateNormal,如果启用taint manager,则zoneNoExecuteTainter速率设置为evictionLimiterQPS,否则,设置zonePodEvictor的速率为evictionLimiterQPS的速率
- 当zone状态为statePartialDisruption,如果启用taint manager,根据zone里的node数量,当node数量大于largeClusterThreshold,设置zoneNoExecuteTainter速率为SecondEvictionLimiterQPS;小于等于largeClusterThreshold,设置zoneNoExecuteTainter速率为0。未启用taint manager,根据zone里的node数量,当node数量大于largeClusterThreshold,设置zonePodEvictor速率为SecondEvictionLimiterQPS;小于等于largeClusterThreshold,设置zonePodEvictorTainter速率为0。
- 当zone状态为stateFullDisruption,如果启用taint manager,则zoneNoExecuteTainter速率设置为evictionLimiterQPS,否则,设置zonePodEvictor的速率为evictionLimiterQPS的速率
- 这里不处理stateInitial状态的zone,因为下一周期,zone会变成非stateInitial,下面就是处理这个情况的
除了上面两种情况,还有一个情况要进行处理,allAreFullyDisrupted为false allWasFullyDisrupted为false,就是没有发生集群所有zone全挂。这个时候zone有可能发生状态转换,所以需要重新评估zone的速率
- 遍历zoneStates,当保存的状态和新的状态不一致的时候–zone状态发生了变化,重新评估zone的速率
- 当zone的状态为stateNormal,如果启用taint manager,则zoneNoExecuteTainter速率设置为evictionLimiterQPS,否则,设置zonePodEvictor的速率为evictionLimiterQPS的速率
- 当zone状态为statePartialDisruption,如果启用taint manager,根据zone里的node数量,当node数量大于largeClusterThreshold,设置zoneNoExecuteTainter速率为SecondEvictionLimiterQPS;小于等于largeClusterThreshold,设置zoneNoExecuteTainter速率为0。未启用taint manager,根据zone里的node数量,当node数量大于largeClusterThreshold,设置zonePodEvictor速率为SecondEvictionLimiterQPS;小于等于largeClusterThreshold,设置zonePodEvictorTainter速率为0。
- 当zone状态为stateFullDisruption,如果启用taint manager,则zoneNoExecuteTainter速率设置为evictionLimiterQPS,否则,设置zonePodEvictor的速率为evictionLimiterQPS的速率
- zoneStates里的状态更新为新的状态
而allAreFullyDisrupted为true allWasFullyDisrupted为true,集群一直都是挂着,不需要处理,zone状态没有发生改变。
6.4.4 总结
只有在这几种情况下,会调整队列速率:
- 集群里所有zone全挂,zone的速率设置为0
- 集群未全挂,zone的unready node比例超过了unhealthyZoneThreshold,且node数量大于largeClusterThreshold,zone的速率设置为SecondEvictionLimiterQPS
其中集群里没有发生的所有zone全挂,某个zone发生全挂,zone的速率还是evictionLimiterQPS


![[译]Kubernetes CRD生成中的那些坑](/translate/kubernetes-crd-generation-pitfalls/crd-gen-pitfall.webp)