Taint Manager源码解析
taint manager是由pod和node事件触发执行,根据node或pod绑定的node是否有的noExcute taint,如果有则对node上所有的pod或这个pod执行删除。
在上篇的node lifecycle controller中,如果启用了taint manager就会调用NewNoExecuteTaintManager对taint manager进行初始化。
在node lifecycle controller中定义了pod事件和node事件的handler,在启用taint manager时候还会将pod事件和node事件放入到taint manager里的nodeUpdateQueue和podUpdateQueue。
同时在node lifecycle controller中会启动一个goroutine 执行taintManager.Run(stopCh)。
kubernetes版本为1.18.6
1 初始化
NewNoExecuteTaintManager定义在pkg\controller\nodelifecycle\scheduler\taint_manager.go
其中nodeUpdateQueue和podUpdateQueue为workqueue。
taintedNodes是存放node上所有的noExecute taint,handlePodUpdate会从taintedNodes查询node的noExecute taint。
taintEvictionQueuetaintEvictionQueue是一个TimedWorkerQueue–定时自动执行队列,介绍见后面。
// NewNoExecuteTaintManager creates a new NoExecuteTaintManager that will use passed clientset to
// communicate with the API server.
func NewNoExecuteTaintManager(c clientset.Interface, getPod GetPodFunc, getNode GetNodeFunc, getPodsAssignedToNode GetPodsByNodeNameFunc) *NoExecuteTaintManager {
eventBroadcaster := record.NewBroadcaster()
recorder := eventBroadcaster.NewRecorder(scheme.Scheme, v1.EventSource{Component: "taint-controller"})
eventBroadcaster.StartLogging(klog.Infof)
if c != nil {
klog.V(0).Infof("Sending events to api server.")
eventBroadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(&v1core.EventSinkImpl{Interface: c.CoreV1().Events("")})
} else {
klog.Fatalf("kubeClient is nil when starting NodeController")
}
tm := &NoExecuteTaintManager{
client: c,
recorder: recorder,
getPod: getPod,
getNode: getNode,
getPodsAssignedToNode: getPodsAssignedToNode,
taintedNodes: make(map[string][]v1.Taint),
nodeUpdateQueue: workqueue.NewNamed("noexec_taint_node"),
podUpdateQueue: workqueue.NewNamed("noexec_taint_pod"),
}
tm.taintEvictionQueue = CreateWorkerQueue(deletePodHandler(c, tm.emitPodDeletionEvent))
return tm
}taintEvictionQueue初始化
func (tc *NoExecuteTaintManager) emitPodDeletionEvent(nsName types.NamespacedName) {
if tc.recorder == nil {
return
}
ref := &v1.ObjectReference{
Kind: "Pod",
Name: nsName.Name,
Namespace: nsName.Namespace,
}
tc.recorder.Eventf(ref, v1.EventTypeNormal, "TaintManagerEviction", "Marking for deletion Pod %s", nsName.String())
}
func deletePodHandler(c clientset.Interface, emitEventFunc func(types.NamespacedName)) func(args *WorkArgs) error {
return func(args *WorkArgs) error {
ns := args.NamespacedName.Namespace
name := args.NamespacedName.Name
klog.V(0).Infof("NoExecuteTaintManager is deleting Pod: %v", args.NamespacedName.String())
if emitEventFunc != nil {
emitEventFunc(args.NamespacedName)
}
var err error
for i := 0; i < retries; i++ {
err = c.CoreV1().Pods(ns).Delete(context.TODO(), name, metav1.DeleteOptions{})
if err == nil {
break
}
time.Sleep(10 * time.Millisecond)
}
return err
}
}
// CreateWorkerQueue creates a new TimedWorkerQueue for workers that will execute
// given function `f`.
func CreateWorkerQueue(f func(args *WorkArgs) error) *TimedWorkerQueue {
return &TimedWorkerQueue{
workers: make(map[string]*TimedWorker),
workFunc: f,
}
}2 数据结构
NoExecuteTaintManager
// NoExecuteTaintManager listens to Taint/Toleration changes and is responsible for removing Pods
// from Nodes tainted with NoExecute Taints.
type NoExecuteTaintManager struct {
client clientset.Interface
recorder record.EventRecorder
// 从informer中获取pod的func
getPod GetPodFunc
// 从informer中获取pod的func
getNode GetNodeFunc
从informer中获取node上的pod的func
getPodsAssignedToNode GetPodsByNodeNameFunc
taintEvictionQueue *TimedWorkerQueue
// keeps a map from nodeName to all noExecute taints on that Node
taintedNodesLock sync.Mutex
taintedNodes map[string][]v1.Taint
// 从nodeUpdateQueue获取的node,会放到这里
nodeUpdateChannels []chan nodeUpdateItem
// 从podUpdateQueue获取的pod,会放到这里
podUpdateChannels []chan podUpdateItem
nodeUpdateQueue workqueue.Interface
podUpdateQueue workqueue.Interface
}其中taintEvictionQueue类型是TimedWorkerQueue。TimedWorkerQueue定义在pkg\controller\nodelifecycle\scheduler\timed_workers.go,它里面包含WorkArgs对象的创建时间、需要被执行的时间,定时器、到期执行的函数。
// TimedWorkerQueue keeps a set of TimedWorkers that are still wait for execution.
type TimedWorkerQueue struct {
sync.Mutex
// map of workers keyed by string returned by 'KeyFromWorkArgs' from the given worker.
workers map[string]*TimedWorker
// 到期要执行的函数
workFunc func(args *WorkArgs) error
}
// TimedWorker is a responsible for executing a function no earlier than at FireAt time.
type TimedWorker struct {
WorkItem *WorkArgs
CreatedAt time.Time
FireAt time.Time
Timer *time.Timer
}
// WorkArgs keeps arguments that will be passed to the function executed by the worker.
type WorkArgs struct {
NamespacedName types.NamespacedName
}NamespacedName定义在staging\src\k8s.io\apimachinery\pkg\types\namespacedname.go
// NamespacedName comprises a resource name, with a mandatory namespace,
// rendered as "<namespace>/<name>". Being a type captures intent and
// helps make sure that UIDs, namespaced names and non-namespaced names
// do not get conflated in code. For most use cases, namespace and name
// will already have been format validated at the API entry point, so we
// don't do that here. Where that's not the case (e.g. in testing),
// consider using NamespacedNameOrDie() in testing.go in this package.
type NamespacedName struct {
Namespace string
Name string
}3 运行
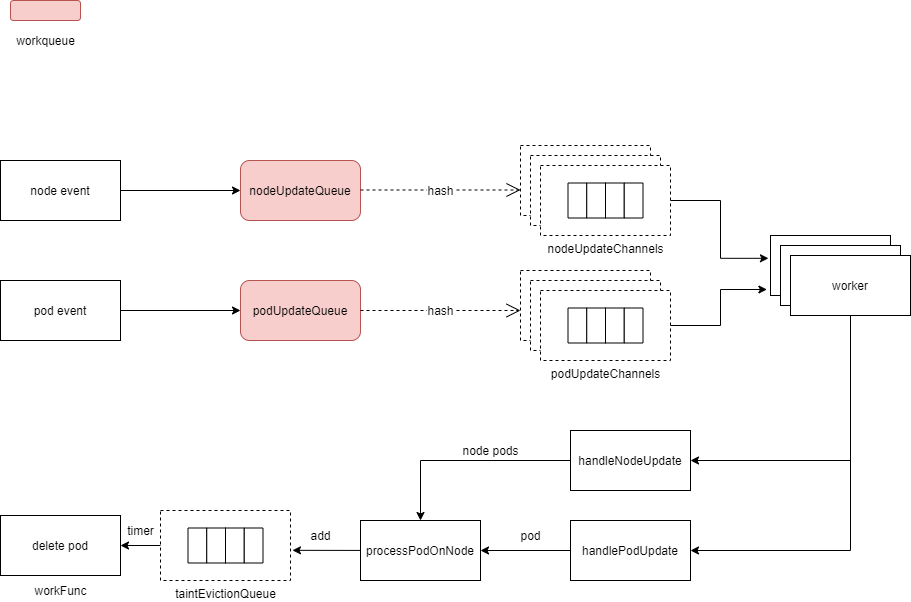
- 创建UpdateWorkerSize个类型为nodeUpdateItem的chan、缓冲区大小为10,chan集合–nodeUpdateChannels;创建UpdateWorkerSize个类型podUpdateItem的chan、缓冲区大小为10,chan集合–podUpdateChannels。其中UpdateWorkerSize为8,NodeUpdateChannelSize为10和podUpdateChannelSize为1。
- 启动一个goroutine,执行从nodeUpdateQueue取一个nodeUpdateItem,丢进其中一个nodeUpdateChannels中,分配的算法是对node name进行hash并跟UpdateWorkerSize取模,获得chan的下标。
- 启动一个goroutine,执行从podUpdateQueue取一个podUpdateItem,丢进其中一个podUpdateChannels,分配算法跟node一样。
- 启动UpdateWorkerSize个goroutine,执行worker方法–处理事件逻辑都在里面。
// Run starts NoExecuteTaintManager which will run in loop until `stopCh` is closed.
func (tc *NoExecuteTaintManager) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
klog.V(0).Infof("Starting NoExecuteTaintManager")
for i := 0; i < UpdateWorkerSize; i++ {
tc.nodeUpdateChannels = append(tc.nodeUpdateChannels, make(chan nodeUpdateItem, NodeUpdateChannelSize))
tc.podUpdateChannels = append(tc.podUpdateChannels, make(chan podUpdateItem, podUpdateChannelSize))
}
// Functions that are responsible for taking work items out of the workqueues and putting them
// into channels.
go func(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
for {
item, shutdown := tc.nodeUpdateQueue.Get()
if shutdown {
break
}
nodeUpdate := item.(nodeUpdateItem)
hash := hash(nodeUpdate.nodeName, UpdateWorkerSize)
select {
case <-stopCh:
tc.nodeUpdateQueue.Done(item)
return
case tc.nodeUpdateChannels[hash] <- nodeUpdate:
// tc.nodeUpdateQueue.Done is called by the nodeUpdateChannels worker
}
}
}(stopCh)
go func(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
for {
item, shutdown := tc.podUpdateQueue.Get()
if shutdown {
break
}
// The fact that pods are processed by the same worker as nodes is used to avoid races
// between node worker setting tc.taintedNodes and pod worker reading this to decide
// whether to delete pod.
// It's possible that even without this assumption this code is still correct.
podUpdate := item.(podUpdateItem)
hash := hash(podUpdate.nodeName, UpdateWorkerSize)
select {
case <-stopCh:
tc.podUpdateQueue.Done(item)
return
case tc.podUpdateChannels[hash] <- podUpdate:
// tc.podUpdateQueue.Done is called by the podUpdateChannels worker
}
}
}(stopCh)
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
wg.Add(UpdateWorkerSize)
for i := 0; i < UpdateWorkerSize; i++ {
go tc.worker(i, wg.Done, stopCh)
}
wg.Wait()
}3.1 worker
消费nodeUpdateChannels和podUpdateChannels里数据,执行handleNodeUpdate和handlePodUpdate。
在事件处理优先级上,node的优先级会高于pod–也就是说如果node事件和pod事件同时发生,则优先处理node事件,等nodeUpdateChannels清空后–即所有node事件处理完,再处理pod事件。
func (tc *NoExecuteTaintManager) worker(worker int, done func(), stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer done()
// When processing events we want to prioritize Node updates over Pod updates,
// as NodeUpdates that interest NoExecuteTaintManager should be handled as soon as possible -
// we don't want user (or system) to wait until PodUpdate queue is drained before it can
// start evicting Pods from tainted Nodes.
for {
select {
case <-stopCh:
return
case nodeUpdate := <-tc.nodeUpdateChannels[worker]:
tc.handleNodeUpdate(nodeUpdate)
tc.nodeUpdateQueue.Done(nodeUpdate)
case podUpdate := <-tc.podUpdateChannels[worker]:
// If we found a Pod update we need to empty Node queue first.
priority:
for {
select {
case nodeUpdate := <-tc.nodeUpdateChannels[worker]:
tc.handleNodeUpdate(nodeUpdate)
tc.nodeUpdateQueue.Done(nodeUpdate)
default:
break priority
}
}
// After Node queue is emptied we process podUpdate.
tc.handlePodUpdate(podUpdate)
tc.podUpdateQueue.Done(podUpdate)
}
}
}3.2 taintEvictionQueue–定时执行队列
上面介绍了taintEvictionQueue的类型TimedWorkerQueue的数据结构,这里说明它是如何工作的,有利于后面理解。
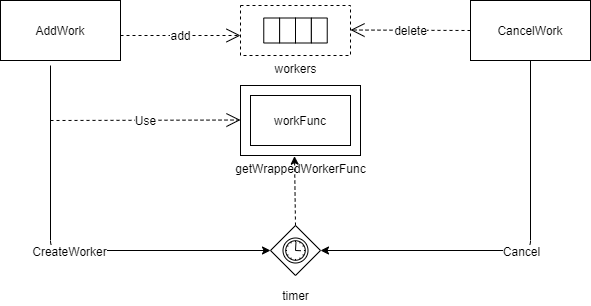
addWork–将pod添加到队列中,并添加一个定时器,到期自动执行包装过的workFunc–这里的workFunc是执行删除pod。
根据key–“podNamespace/podName”,判断pod是否已经在队列里面了–workers中是否已经添加过了这个pod,已经有了直接返回。比如之前node发生更新,之后又发生更新事件,这样就会重复的调用addWork。
执行CreateWorker创建worker–设置创建时间、执行时间、定时器、定时触发执行的func。
将创建的worker保存到workers中。
定义在pkg\controller\nodelifecycle\scheduler\timed_workers.go
// AddWork adds a work to the WorkerQueue which will be executed not earlier than `fireAt`. func (q *TimedWorkerQueue) AddWork(args *WorkArgs, createdAt time.Time, fireAt time.Time) { key := args.KeyFromWorkArgs() klog.V(4).Infof("Adding TimedWorkerQueue item %v at %v to be fired at %v", key, createdAt, fireAt) q.Lock() defer q.Unlock() if _, exists := q.workers[key]; exists { klog.Warningf("Trying to add already existing work for %+v. Skipping.", args) return } worker := CreateWorker(args, createdAt, fireAt, q.getWrappedWorkerFunc(key)) q.workers[key] = worker }KeyFromWorkArgs()–这里输出的格式是"namespace/name",即“podNamespace/podName”。
// 定义在pkg\controller\nodelifecycle\scheduler\timed_workers.go // KeyFromWorkArgs creates a key for the given `WorkArgs` func (w *WorkArgs) KeyFromWorkArgs() string { return w.NamespacedName.String() } // 定义在staging\src\k8s.io\apimachinery\pkg\types\namespacedname.go const ( Separator = '/' ) // String returns the general purpose string representation func (n NamespacedName) String() string { return fmt.Sprintf("%s%c%s", n.Namespace, Separator, n.Name) }**getWrappedWorkerFunc(key)**返回一个
func(args *WorkArgs) error–对workFunc进行包装,其中workFunc在taint manager初始化里定义了执行删除pod(上面初始化段落里说明)。这里面返回包装函数执行逻辑:
- 执行workFunc
- 执行成功,将key在workers中保存的信息设置成nil。为什么要设置成nil,是因为在 AddWork中会判断key是否已经在队列中,防止执行完删除pod之后又被添加进队列–感觉这是预防性编程。执行成功的key,没有执行cancelWorkWithEvent不会再添加进来。
- 执行不成功,从workers中删除这个key。这样后面还可以添加到队列里。
定义在pkg\controller\nodelifecycle\scheduler\timed_workers.go
func (q *TimedWorkerQueue) getWrappedWorkerFunc(key string) func(args *WorkArgs) error { return func(args *WorkArgs) error { err := q.workFunc(args) q.Lock() defer q.Unlock() if err == nil { // To avoid duplicated calls we keep the key in the queue, to prevent // subsequent additions. q.workers[key] = nil } else { delete(q.workers, key) } return err } }CreateWorker–创建一个worker,并执行包装过的workFunc。
如果fireAt时间在createdat时间之前,说明应该立即执行,所以起一个goroutine执行上面包装过的workFunc。
否则使用time.AfterFunc起一个定时器,在fireAt-createdAt时间后,启动一个goroutine执行上面包装过的workFunc。这个是自执行队列的关键,这就是TimedWorkerQueue队列,为什么不需要func来消费。
返回一个TimedWorker。
定义在pkg\controller\nodelifecycle\scheduler\timed_workers.go
// CreateWorker creates a TimedWorker that will execute `f` not earlier than `fireAt`. func CreateWorker(args *WorkArgs, createdAt time.Time, fireAt time.Time, f func(args *WorkArgs) error) *TimedWorker { delay := fireAt.Sub(createdAt) if delay <= 0 { go f(args) return nil } timer := time.AfterFunc(delay, func() { f(args) }) return &TimedWorker{ WorkItem: args, CreatedAt: createdAt, FireAt: fireAt, Timer: timer, } }CancelWork–pod从队列中移除
判断key是否在workers中,如果存在且不为nil,说明还未执行,则执行Cancel()–终止worker中的定时器,wokers中移除这个key。
定义在pkg\controller\nodelifecycle\scheduler\timed_workers.go
// CancelWork removes scheduled function execution from the queue. Returns true if work was cancelled. func (q *TimedWorkerQueue) CancelWork(key string) bool { q.Lock() defer q.Unlock() worker, found := q.workers[key] result := false if found { klog.V(4).Infof("Cancelling TimedWorkerQueue item %v at %v", key, time.Now()) if worker != nil { result = true worker.Cancel() } delete(q.workers, key) } return result } // Cancel cancels the execution of function by the `TimedWorker` func (w *TimedWorker) Cancel() { if w != nil { w.Timer.Stop() } }
3.3 handleNodeUpdate–处理node事件
依次遍历node上的pod,判断pod的toleration是否能容忍node上的noExcute taint,不能完全容忍则直接删除pod,能够完全容忍则等待最小tolerationSeconds,然后执行删除pod。
- 从informer中获取node信息,如果node不存在–说明node被删除了,则从taintedNodes中将node删除;如果是其他错误,直接返回。这里为什么要taintedNodes里删除这个node?因为后面handlePodUpdate会从taintedNodes里获取node的noExcute taint–node不存在肯定没有taint。
- 将node的noExcute taint保存到taintedNodes中。判断node是否有noExcute taint,如果没有则从taintedNodes中将node删除,同时将node上的所有pod从taintEvictionQueue中移除–执行cancelWorkWithEvent,然后返回–无需处理这个node;否则保存node的noExcute taint到taintedNodes中。
- 判断node上是否有pod,如果没有pod则直接返回。
- 对node上的所有pod,依次执行processPodOnNode–pod上的noExcute toleration是否都能容忍node上的noExcute taint,如果不能则删除pod;如果能,则等待toleration里最小的时间后删除pod。
定义在pkg\controller\nodelifecycle\scheduler\taint_manager.go
//执行驱逐node上面的pod--不能容忍node的tains
func (tc *NoExecuteTaintManager) handleNodeUpdate(nodeUpdate nodeUpdateItem) {
node, err := tc.getNode(nodeUpdate.nodeName)
if err != nil {
if apierrors.IsNotFound(err) {
// Delete
klog.V(4).Infof("Noticed node deletion: %#v", nodeUpdate.nodeName)
tc.taintedNodesLock.Lock()
defer tc.taintedNodesLock.Unlock()
delete(tc.taintedNodes, nodeUpdate.nodeName)
return
}
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("cannot get node %s: %v", nodeUpdate.nodeName, err))
return
}
// Create or Update
klog.V(4).Infof("Noticed node update: %#v", nodeUpdate)
taints := getNoExecuteTaints(node.Spec.Taints)
func() {
tc.taintedNodesLock.Lock()
defer tc.taintedNodesLock.Unlock()
klog.V(4).Infof("Updating known taints on node %v: %v", node.Name, taints)
if len(taints) == 0 {
delete(tc.taintedNodes, node.Name)
} else {
tc.taintedNodes[node.Name] = taints
}
}()
// This is critical that we update tc.taintedNodes before we call getPodsAssignedToNode:
// getPodsAssignedToNode can be delayed as long as all future updates to pods will call
// tc.PodUpdated which will use tc.taintedNodes to potentially delete delayed pods.
pods, err := tc.getPodsAssignedToNode(node.Name)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf(err.Error())
return
}
if len(pods) == 0 {
return
}
// Short circuit, to make this controller a bit faster.
if len(taints) == 0 {
klog.V(4).Infof("All taints were removed from the Node %v. Cancelling all evictions...", node.Name)
for i := range pods {
tc.cancelWorkWithEvent(types.NamespacedName{Namespace: pods[i].Namespace, Name: pods[i].Name})
}
return
}
now := time.Now()
for _, pod := range pods {
podNamespacedName := types.NamespacedName{Namespace: pod.Namespace, Name: pod.Name}
tc.processPodOnNode(podNamespacedName, node.Name, pod.Spec.Tolerations, taints, now)
}
}3.3.1 cancelWorkWithEvent
从taintEvictionQueue中移除pod的work,移除成功就发送一个取消pod驱逐event。
定义在pkg\controller\nodelifecycle\scheduler\taint_manager.go
func (tc *NoExecuteTaintManager) cancelWorkWithEvent(nsName types.NamespacedName) {
if tc.taintEvictionQueue.CancelWork(nsName.String()) {
tc.emitCancelPodDeletionEvent(nsName)
}
}
func (tc *NoExecuteTaintManager) emitCancelPodDeletionEvent(nsName types.NamespacedName) {
if tc.recorder == nil {
return
}
ref := &v1.ObjectReference{
Kind: "Pod",
Name: nsName.Name,
Namespace: nsName.Namespace,
}
tc.recorder.Eventf(ref, v1.EventTypeNormal, "TaintManagerEviction", "Cancelling deletion of Pod %s", nsName.String())
}3.3.2 processPodOnNode
对taint和toleration进行比较,判断出是否能够完全容忍taint。如果不能完全容忍,立即删除pod。否则等待能够容忍的toleration中的tolerationSeconds最小时间,然后执行删除pod。
- 判断taint是否为空,为空就执行cancelWorkWithEvent–队列中移除这个pod的worker。
- 对taint和toleration进行比较,判断出是否能够完全容忍taint。如果不能完全容忍,那就先执行cancelWorkWithEvent–防止如果pod已经在队列中,不能添加到队列中去;然后执行AddWork,设置created、fired时间为现在–立即执行删除pod。
- 执行getMinTolerationTime计算能够容忍的toleration中的tolerationSeconds最小时间
- 判断是否在队列中已经存在这个pod的worker,如果存在则判断原来的created时间,是否是过去时间,如果是过去时间,直接返回–维持原来的worker执行;不是过去时间则执行cancelWorkWithEvent–移除存在的pod worker。
- 执行AddWork,设置created为现在、fired时间为现在时间+最小的tolerationSeconds。
定义在pkg\controller\nodelifecycle\scheduler\taint_manager.go
func (tc *NoExecuteTaintManager) processPodOnNode(
podNamespacedName types.NamespacedName,
nodeName string,
tolerations []v1.Toleration,
taints []v1.Taint,
now time.Time,
) {
if len(taints) == 0 {
tc.cancelWorkWithEvent(podNamespacedName)
}
allTolerated, usedTolerations := v1helper.GetMatchingTolerations(taints, tolerations)
if !allTolerated {
klog.V(2).Infof("Not all taints are tolerated after update for Pod %v on %v", podNamespacedName.String(), nodeName)
// We're canceling scheduled work (if any), as we're going to delete the Pod right away.
// 先在taintEvictionQueue移除该podNamespacedName,因为AddWork中会判断如果在队列中,不能再添加了,我们要重置create time, fired time。
tc.cancelWorkWithEvent(podNamespacedName)
//taintEvictionQueue里面包含了定时器,定时器触发执行处理函数,所以不需要其他func来处理这个队列
tc.taintEvictionQueue.AddWork(NewWorkArgs(podNamespacedName.Name, podNamespacedName.Namespace), time.Now(), time.Now())
return
}
minTolerationTime := getMinTolerationTime(usedTolerations)
// getMinTolerationTime returns negative value to denote infinite toleration.
if minTolerationTime < 0 {
klog.V(4).Infof("New tolerations for %v tolerate forever. Scheduled deletion won't be cancelled if already scheduled.", podNamespacedName.String())
return
}
startTime := now
triggerTime := startTime.Add(minTolerationTime)
scheduledEviction := tc.taintEvictionQueue.GetWorkerUnsafe(podNamespacedName.String())
if scheduledEviction != nil {
startTime = scheduledEviction.CreatedAt
//startTime在现在之前,代表work在过去创建的,之前触发驱逐, 合法不做任何操作,保留原来的work
if startTime.Add(minTolerationTime).Before(triggerTime) {
return
}
//work创建时间在未来/现在,取消原来的work,新建一个work
tc.cancelWorkWithEvent(podNamespacedName)
}
tc.taintEvictionQueue.AddWork(NewWorkArgs(podNamespacedName.Name, podNamespacedName.Namespace), startTime, triggerTime)
}3.4 handlePodUpdate
判断pod的toleration是否能够容忍node上的noExcute taint,如果不能完全容忍则直接删除这个pod,能够完全容忍则等待最小的tolerationSeconds时间,然后删除pod。
- 从informer中获取pod信息,如果pod不存在–说明pod被已经删除了,则执行cancelWorkWithEvent–从队列中将pod worker移除。如果发生其他错误,直接返回。
- 检查pod绑定的node是否发生改变,如果改变了,直接返回
- 检查node name是否为空,代表pod还未被调度,直接返回。
- 检查node是否有noExcute taint–从taintedNodes里获取node的noExcute taint,如果没有,说明node被删除或者node没有noExcute taint,直接返回。这也是在handleNodeUpdate里,更新taintedNodes原因。
- 执行processPodOnNode


![[译]Kubernetes CRD生成中的那些坑](/translate/kubernetes-crd-generation-pitfalls/crd-gen-pitfall.webp)